The Journey of Coinbase
Coinbase was founded in June 2012 by Brian Armstrong and Fred Ehrsam in San Francisco, California. It started with a simple vision: to make it easy for anyone to buy, sell, and store digital currencies like Bitcoin.
The founders saw the potential in the cryptocurrency space, which was emerging as a disruptive force in the financial world. In its early years, Coinbase faced challenges related to security and regulatory issues, but it quickly gained traction as the go-to platform for individuals and institutions looking to get involved in the crypto market. In 2021, Coinbase went public through a direct listing on the NASDAQ, solidifying its position as a leader in the cryptocurrency exchange space.
Today, Coinbase is one of the most widely used cryptocurrency exchanges in the world, providing services in over 100 countries. It continues to expand its offerings, including features like staking, lending, and custody services. Let’s go with the Coinbase Business Model.
Coinbase’s Struggles
Like any company, Coinbase faced its share of struggles along the way. Some of the key challenges include:
Regulatory Issues:
The cryptocurrency market is heavily scrutinized by regulatory authorities around the world. Coinbase has faced issues with compliance, including pressure from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to comply with regulations regarding the listing of digital assets and the classification of cryptocurrencies.
Security Concerns:
As a platform that stores billions of dollars worth of digital assets, Coinbase has been a target for hackers. While the company has continuously worked on improving its security measures, there have been notable incidents where customers’ funds were compromised.
Market Volatility:
Cryptocurrencies are notorious for their volatility, and Coinbase’s revenue is closely tied to market conditions. During periods of market downturns, the company has seen a reduction in trading volume, which affects its overall profitability.
Competition:
Coinbase operates in a highly competitive space, with many other exchanges offering similar services. Binance, Kraken, and Gemini are just a few of Coinbase’s direct competitors, each with their own unique features and offerings.
Coinbase Stats and Facts
- Founded: June 2012
- Headquarters: San Francisco, California
- Users: Over 73 million verified users (as of 2021)
- Supported Assets: Over 100 cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, etc.)
- Revenue: Coinbase generated $7.8 billion in revenue in 2021, up from $1.3 billion in 2020.
- Market Cap: Coinbase’s market capitalization exceeded $85 billion as of its public debut in 2021.
- Global Reach: Available in over 100 countries worldwide.
- Assets Under Custody: Over $180 billion in customer assets were held by Coinbase in 2021.
How Does Coinbase Work?
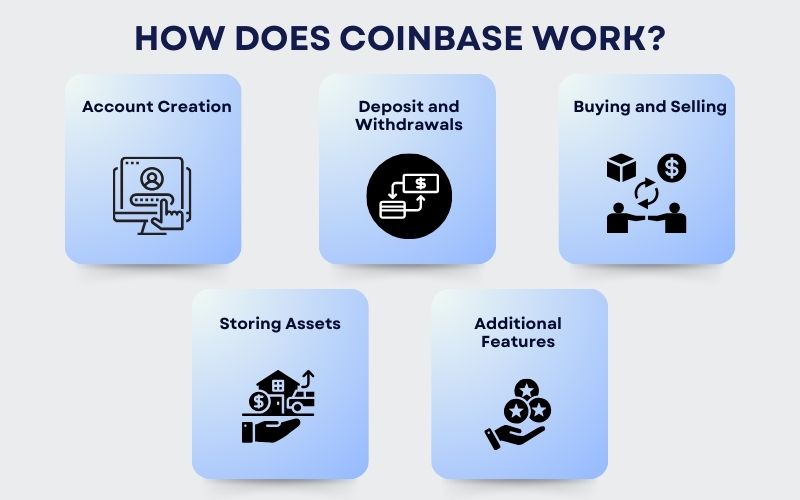 Coinbase operates as an online cryptocurrency exchange platform where users can buy, sell, and store digital currencies. The process works as follows:
Coinbase operates as an online cryptocurrency exchange platform where users can buy, sell, and store digital currencies. The process works as follows:
Account Creation:
Users create an account on Coinbase and go through a verification process to ensure compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations.
Deposit and Withdrawals:
Once verified, users can deposit funds into their Coinbase accounts using a bank transfer, credit card, or debit card. Similarly, users can withdraw funds to their linked bank accounts or external cryptocurrency wallets.
Buying and Selling:
Users can place market or limit orders to buy and sell cryptocurrencies. Coinbase allows for both one-time purchases as well as recurring buys.
Storing Assets:
Coinbase provides a secure wallet for users to store their digital currencies. Coinbase also offers a separate service called Coinbase Custody, aimed at institutional clients who require more advanced storage solutions.
Additional Features:
Over the years, Coinbase has expanded its features, adding options for staking, margin trading, and a standalone app (Coinbase Pro) that caters to advanced traders.
Account Confirmation and Verification
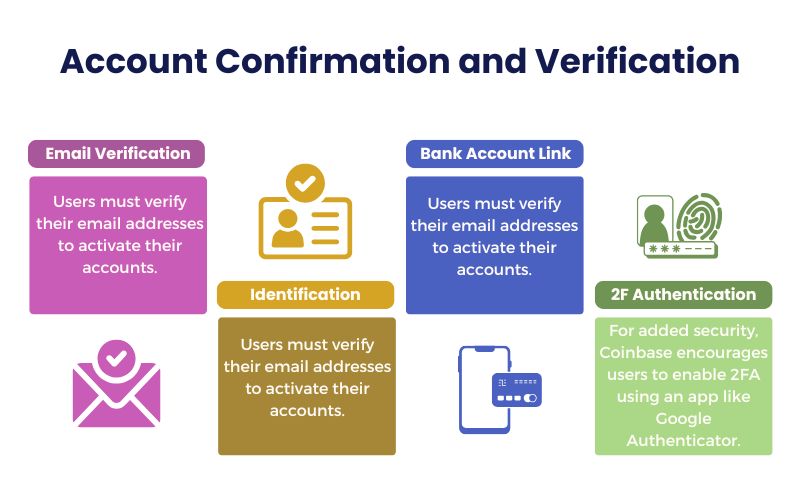 For security and regulatory reasons, Coinbase requires users to confirm their identity. The process typically involves:
For security and regulatory reasons, Coinbase requires users to confirm their identity. The process typically involves:
- Email Verification: Users must verify their email addresses to activate their accounts.
- Personal Identification: Users must submit proof of identity, such as a driver’s license or passport. This step is essential to comply with KYC regulations and prevent fraud.
- Bank Account Link: Users link their bank accounts to facilitate deposits and withdrawals, which is another step in verifying their identity.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): For added security, Coinbase encourages users to enable 2FA using an app like Google Authenticator.
A Coinbase Business Model
Coinbase’s business model revolves around providing a platform for trading, storing, and managing cryptocurrencies. The company generates revenue through the following primary streams:
Transaction Fees:
Coinbase generates a significant portion of its revenue through transaction fees. When users buy or sell cryptocurrencies, the platform charges a spread (a small markup or markdown on the market price). Additionally, Coinbase applies a transaction fee that varies based on the transaction amount and the payment method. These fees can range from 1.49% for credit card payments to 3.99% for instant card purchases. The fees are a core revenue stream, particularly from retail users.
Coinbase Pro:
Coinbase Pro is designed for experienced traders, offering advanced features and lower fees compared to the standard Coinbase platform. Pro users benefit from a fee structure that rewards higher trading volumes with reduced rates. This platform caters to professional traders who need more sophisticated tools, such as real-time charts, order book data, and margin trading. The reduced fees help Coinbase attract institutional and high-volume traders, contributing to a portion of their overall revenue.
Staking Services:
Coinbase provides staking services, allowing users to participate in proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains, such as Ethereum 2.0. Staking allows users to earn rewards by helping maintain the network’s security and operations. Coinbase charges a commission on the rewards earned by users through staking. This provides a steady revenue stream for Coinbase while offering users an opportunity to passively earn income on their digital assets.
Institutional Services:
Coinbase offers a suite of services for institutional clients, such as large investors, hedge funds, and financial institutions. These services include custodial solutions, high-volume trading platforms, and over-the-counter (OTC) trading desks. Coinbase Custody, a specialized service for institutional clients, enables secure storage of large amounts of digital assets. By catering to this niche market, Coinbase generates substantial fees from high-net-worth clients and large institutions.
Interest on Cash Balances:
Coinbase earns interest by holding funds in cash or liquid assets on behalf of users. For retail and institutional clients, Coinbase provides a custodial service that allows it to manage cash reserves. The company then uses these funds in short-term investments or liquidity pools to generate interest. Coinbase can share a portion of this interest with its users, but it retains a significant share as part of its revenue model. This is a more passive, but increasingly important, revenue stream as the platform grows.
How Coinbase Makes Money
As mentioned, Coinbase’s revenue primarily comes from transaction fees, but other key ways the company generates income include:
Trading Fees:
When users make transactions (buying, selling, or exchanging cryptocurrencies), Coinbase charges a fee based on the amount traded and the payment method. The fees are higher for retail users compared to institutional traders on Coinbase Pro.
Staking Rewards:
Coinbase allows users to stake certain assets and earns a fee for facilitating staking. Users who stake cryptocurrencies like Ethereum 2.0 through Coinbase receive a portion of the staking rewards, but Coinbase retains a percentage for providing the service.
Institutional Services:
Coinbase serves institutional clients, offering a range of products such as trading services, custody, and portfolio management. These high-value services generate significant revenue.
Interest on Deposits:
Coinbase also earns income by keeping user funds in cash or liquid assets.
How Much Does it Cost to Develop an App Like Coinbase?
Developing an app like Coinbase requires significant investment in technology, security, and regulatory compliance. The cost of developing such an app can vary depending on the features, security measures, and geographical regions involved.
- Development Costs: A basic cryptocurrency exchange platform could cost anywhere between $50,000 to $200,000 to develop, depending on the complexity of the app, the technology stack, and the team involved.
- Security Features: Incorporating robust security measures, such as multi-signature wallets, 2FA, and end-to-end encryption, could raise costs by an additional $100,000 to $300,000.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Updates: After development, ongoing maintenance, updates, and regulatory compliance could cost between $20,000 to $50,000 annually.
- Compliance and Licensing: Depending on the jurisdiction, obtaining the necessary licenses to operate as a cryptocurrency exchange could be a significant cost factor. This could range from $100,000 to $500,000 or more, depending on the country.
Conclusion
Coinbase has successfully positioned itself as one of the leading platforms in the cryptocurrency exchange market. Despite facing challenges like regulatory hurdles, security risks, and competition, the company has continually adapted its business model to cater to a broad range of users, from retail investors to institutional clients.
With a diversified revenue stream, including transaction fees, staking, and institutional services, Coinbase’s business model shows that there’s significant potential in the evolving cryptocurrency space.
As digital currencies continue to grow in popularity, Coinbase’s role as a trusted exchange and financial service provider is likely to expand. In this evolving landscape, platforms such as Silver WebBuzz are also emerging as key players, offering innovative solutions and services that contribute to the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.




